Pq+qp
But in this case, :(p!q) will be true.

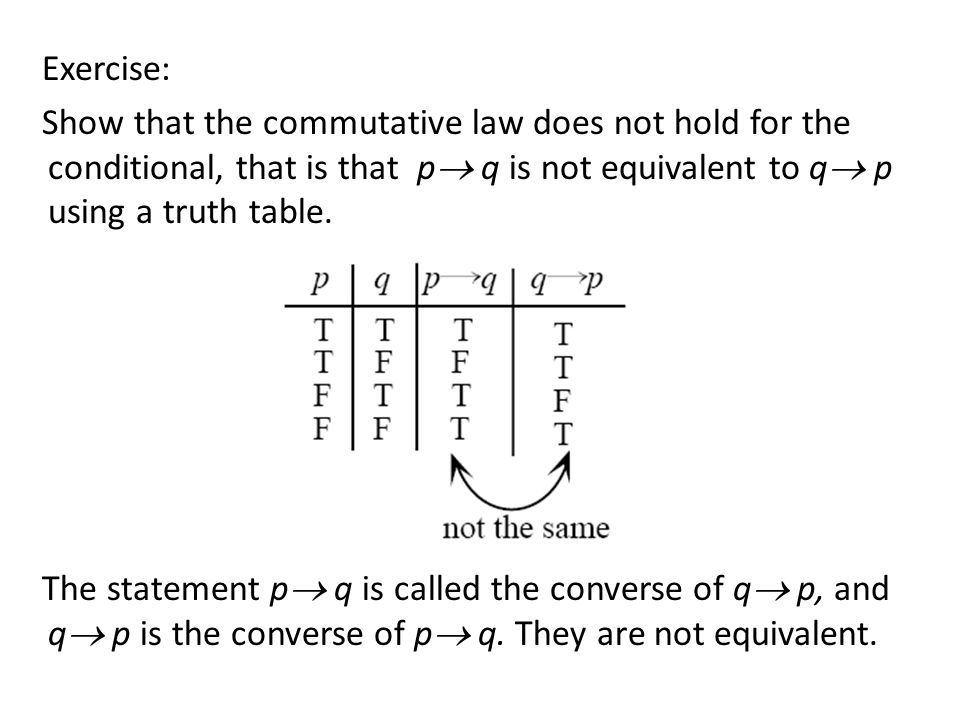
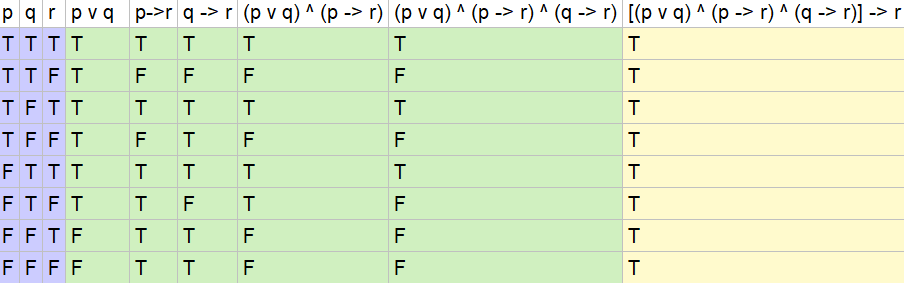
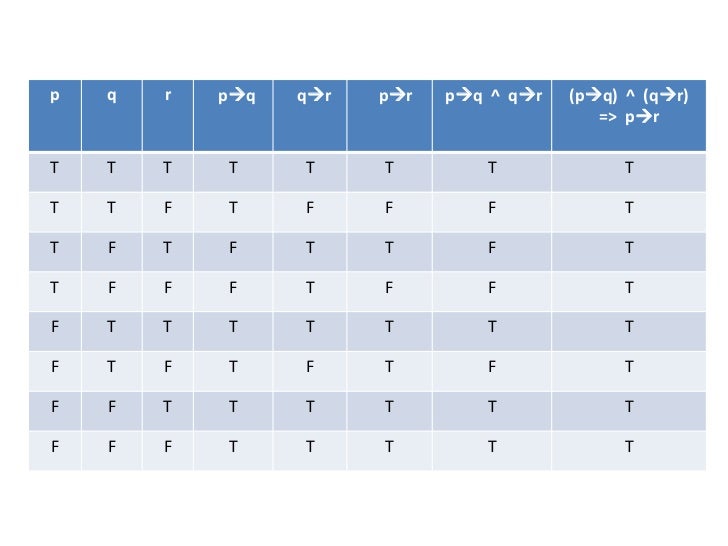
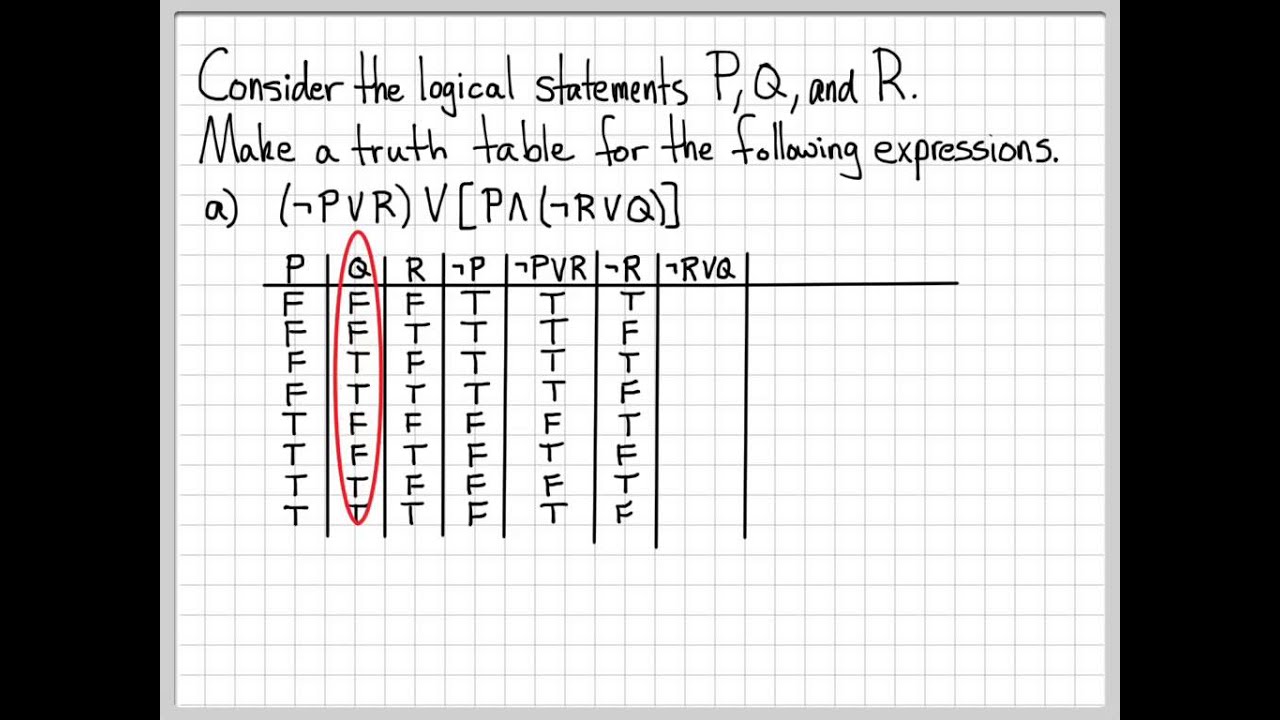
Pq+qp. If I am elected then I will lower the taxes If you get 100% on the final then you will get an A p:. (pVq) V (~p^q) → q p q ~p p V q ~p ^ q (p V q) V (~p ^ q) (p V q) V (~p ^ q) → q T T F T F T T T F F T F T F F T T T T T T F F T F F F T Problem 18:. (~r∧(p→~q))→p≡r∨p So, if we ever encounter(~r∧(p→~q))→p, we can replace it with r∨p without changing the logical meaning of the statement!.
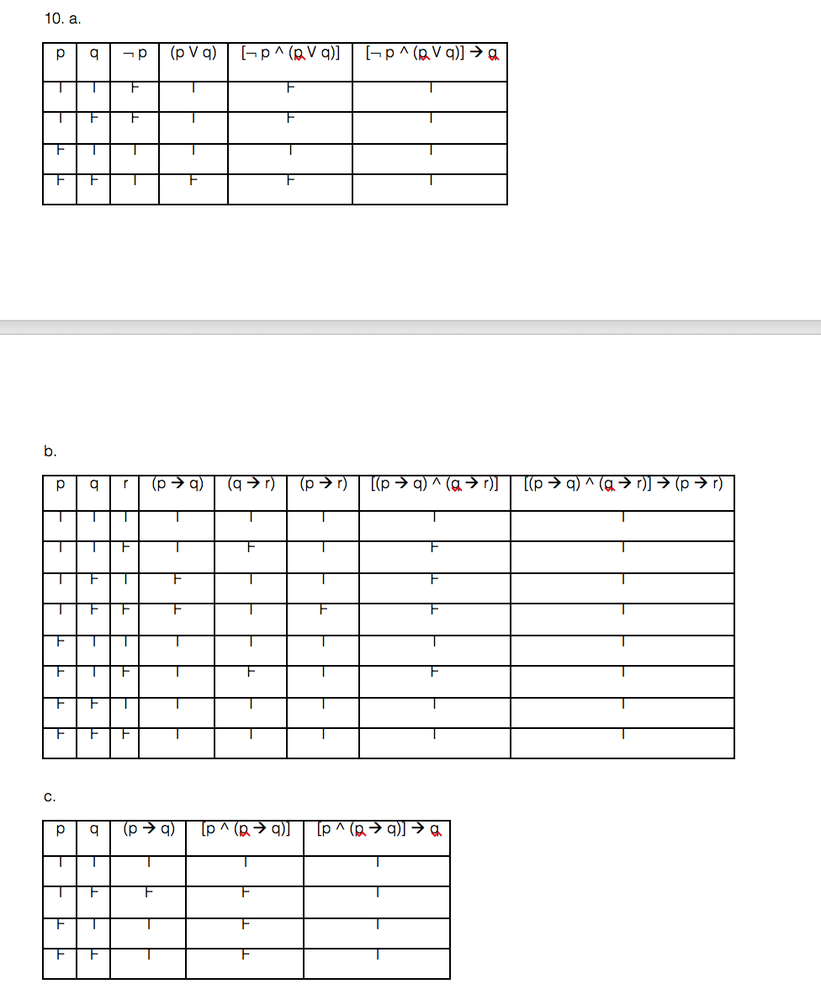
Show that each implication in Exercise 10 is a tautol-. The children were told to mind their p's and q's. Hence this case is not possible.
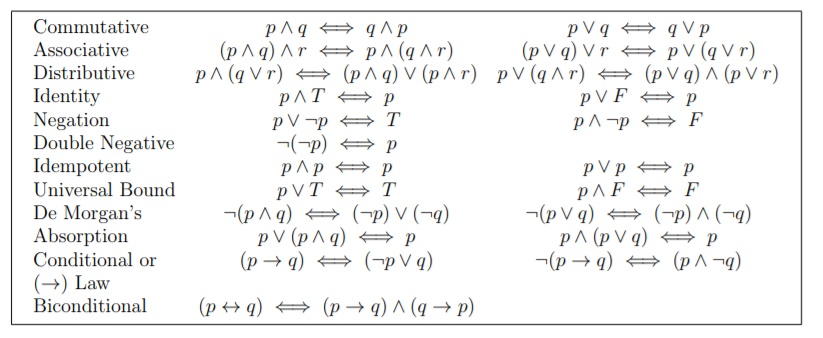
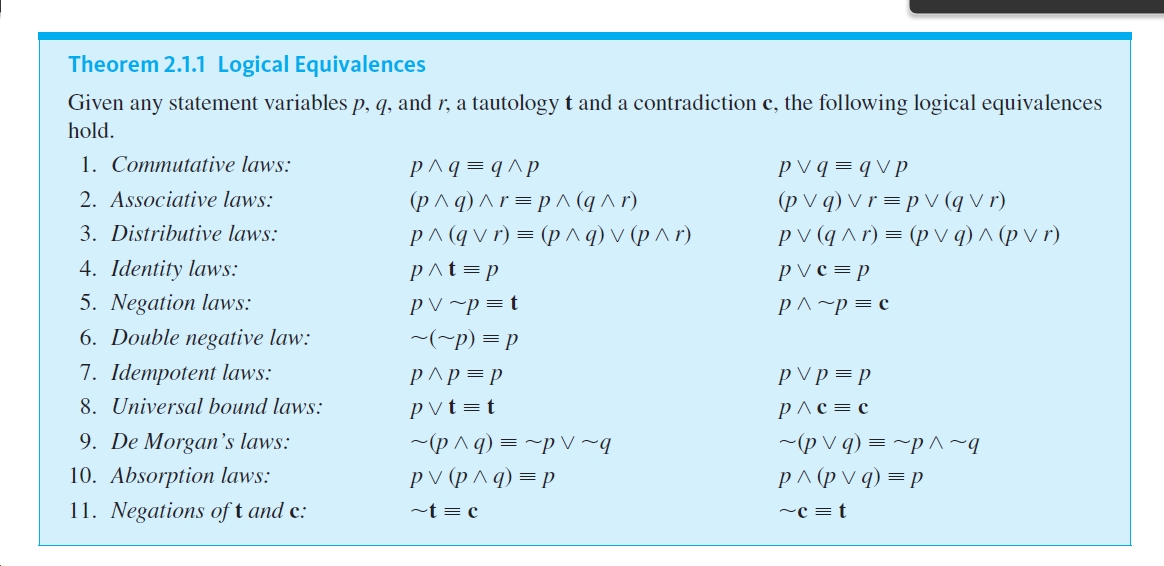
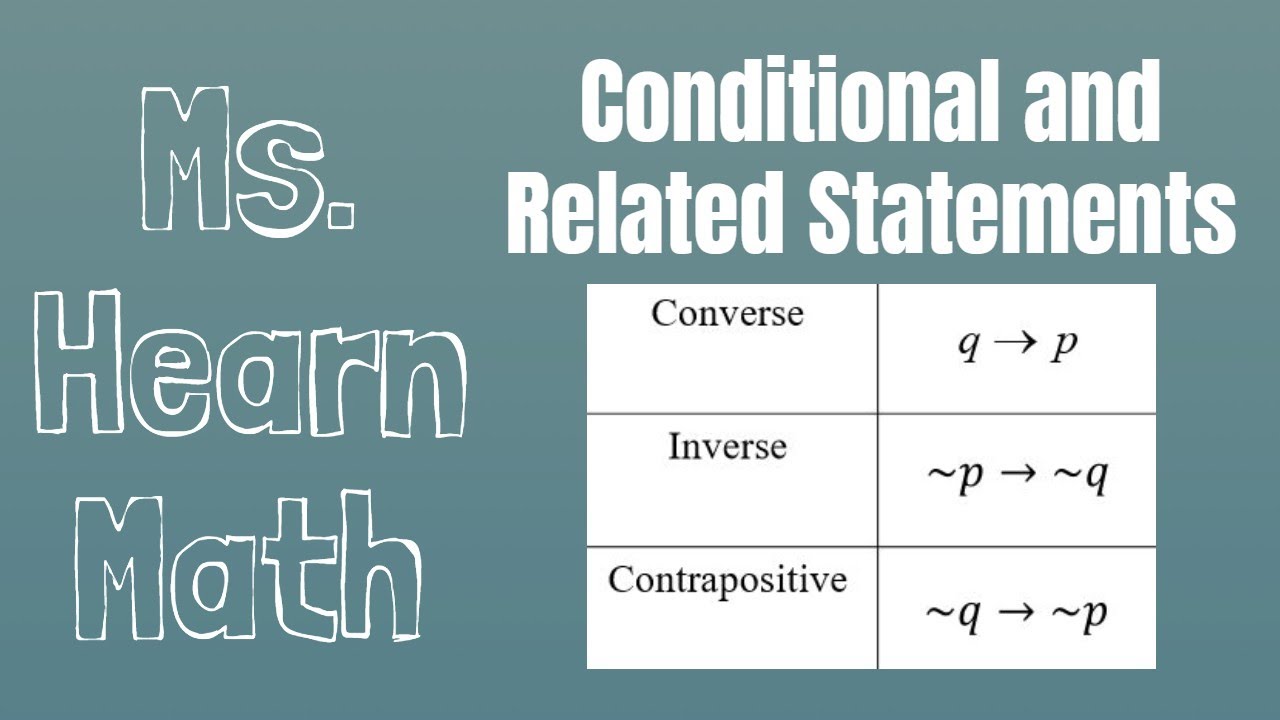
Converse Inverse Contrapositive- For a statement p → q, q → p is a converse statement, ∼p → ∼q is a inverse statement, ∼q → ∼p is contrapositive statement. Discrete Mathematics I (Fall 14) 1.3 Propositional Equivalences Tautologies, Contradictions, and Contingencies A tautology is a compound proposition which is always true. In logic and mathematics, statements p {\displaystyle p} and q {\displaystyle q} are said to be logically equivalent if they are provable from each other under a set of axioms, or have the same truth value in every model.
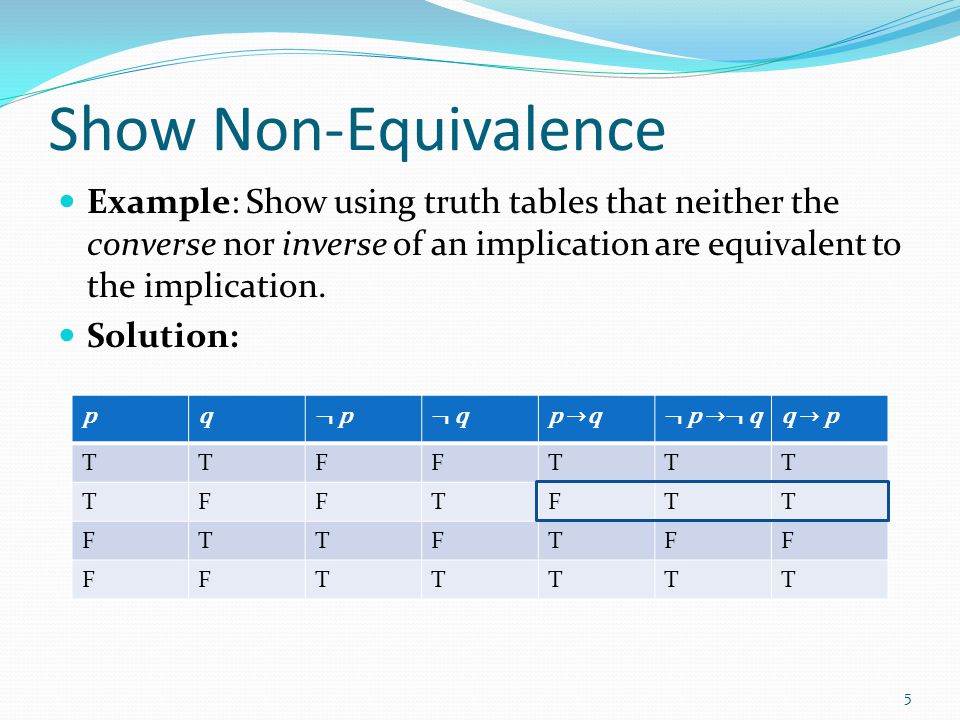
Non-equivalence Prove that each of the following pairs of propositional formulae are not equivalent by finding an input theydifferon. Pq I study or I fail. Problems based on Converse, Inverse and Contrapositive.
Determine the truth values of the given statements. The logical equivalence of p {\displaystyle p} and q {\displaystyle q} is sometimes expressed as p ≡ q {\displaystyle p\equiv q}, p::. Therefore if p is true then q and r are true De Morgan’s eorem (Ô) ¬(p∧q).
Más videos sobre LÓGICA https://w. Con Tablas de la Verdad se analiza una Proposición Lógica para saber si es una tautologia o contradicción o contingencia. Is (q∧ (p ¬q)) ¬p a tautology?.
The Negation of a Conditional Statement. Suppose :(p!q) is false and p^:qis true. Therefore the disjunction (p or q) is true Composition (p → q) (p → r) ∴ (p → (q∧r)) if p then q;.
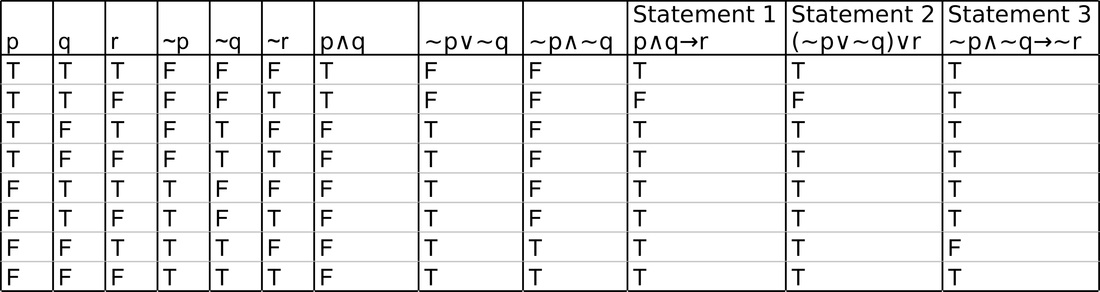
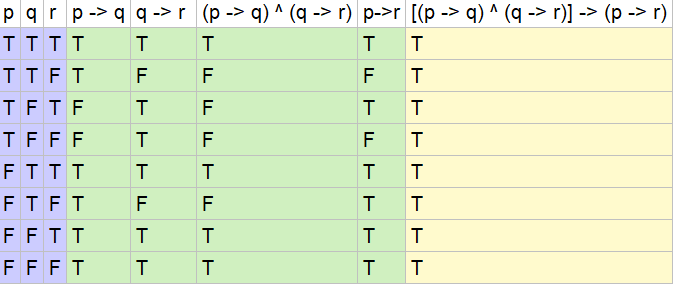
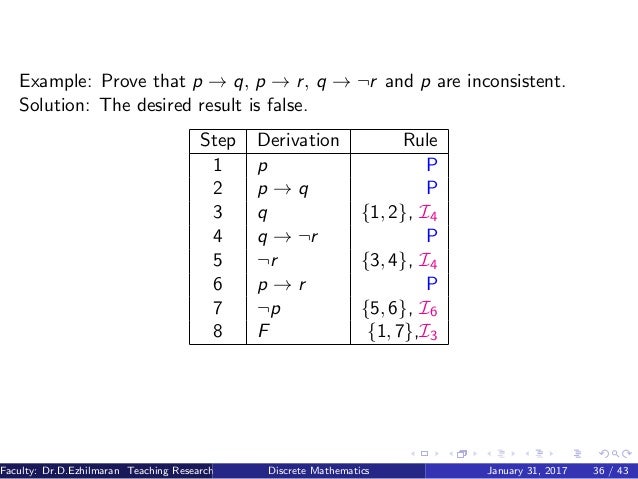
Marked higher sales, bolstered by strong performance in both the food and distribution businesses, it said. Show that the argument form with premises (p ∧ t) → (r∨s), q→(u∧t), u→p, and ¬s and conclusion q → r is valid by first using Exercise 11 and then us- ing rules of inference from Table 1. Since (p ^q) !:p _:q is T in all cases, therefore (p^q) :p_:q.
You have a typo on the third line:. I am elected q:. In this case, the truth values for (~r∧(p→~q))→p and r∨p are exactly the same, so we can conclude that the two statements are equivalent:.
(p^q)_(:p^q)_:q (q ^(p_:p))_:q Comm.,Assoc.,Distrib. (q ^T)_:q Negation q _:q Identity T Negation 2. Only when both P and Q are true but R is false;. Let P − “He studies very hard” Let Q − “He is the best boy in the class” Therefore − "He studies very hard and he is the best boy in the class" Simplification.
Answered Given a conditional statement p → q, which statement is logically equivalent?. This is the principle that, from a contradiction, anything (and everything) follows as a logical conclusion. The table below explores the four possible cases, but the truth is simpler than that.
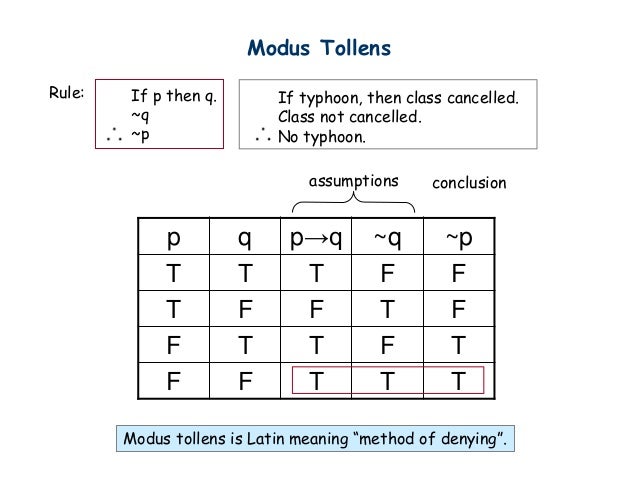
We can use a truth table to verify the claim. Implication can be expressed by disjunction and negation:. ~p → ~q ~q → ~p.
Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework. Show that \((p \Rightarrow q) \Leftrightarrow (\overline{q} \Rightarrow \overline{p})\) is a tautology. A) A = (p_q) !(p q) p q p_q p q A.
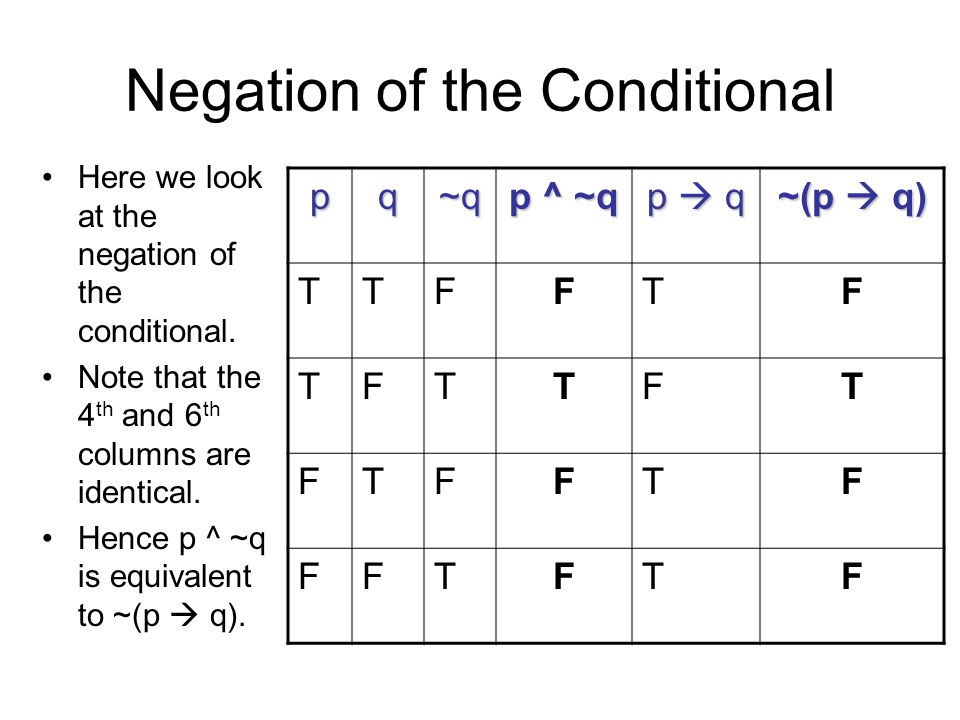
$$\begin{matrix} P \\ Q \\ \hline \therefore P \land Q \end{matrix}$$ Example. The logical equivalency \(\urcorner (P \to Q) \equiv P \wedge \urcorner Q\) is interesting because it shows us that the negation of a conditional statement is not another conditional statement.The negation of a conditional statement can be written in the form of a conjunction. Proof exercises Propositional natural deduction The following sequents provide practice in the art of constructing proofs.
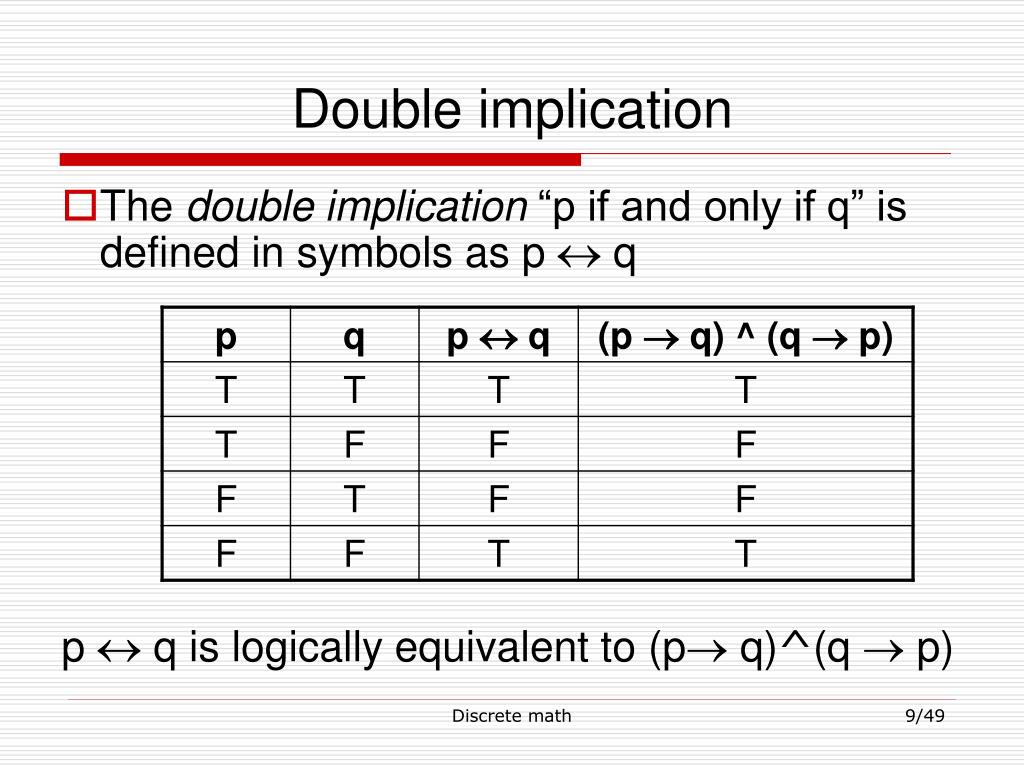
P^:qis true only if pis true and qis false. Since the letters in the press were reversed (so they'd print forward), the printmaker (or typographer) needed to be careful not to confuse one letter for the other. P ↔ q ≡ (p → q)∧(q → p) So, for instance, saying that “John is married if and only if he has a spouse” is the same as saying “if John is married then he has a spouse”.
Demostrar que la proposición ( p ↔ q ) ↔ ¬ (p → q) ʌ (q → p) es una Contradicción, para demostrarlo, debemos construir la tabla de verdad y verificar que efectivamente la función lógica es falsa para todos los casos:. P → ∼ Q Q →∼ P ∴ P ∨ Q Use The Truth Table Below To Determine Whether This Form Of Argument Is Valid Or Invalid. Suppose :(p!q) is true and p^:qis false.:(p!q) would be true if p!qis false.
Therefore they are true conjointly Addition p ∴ (p∨q) p is true;. Maybe that was bothering you?. Simple and best practice solution for 3(p+q)=p equation.
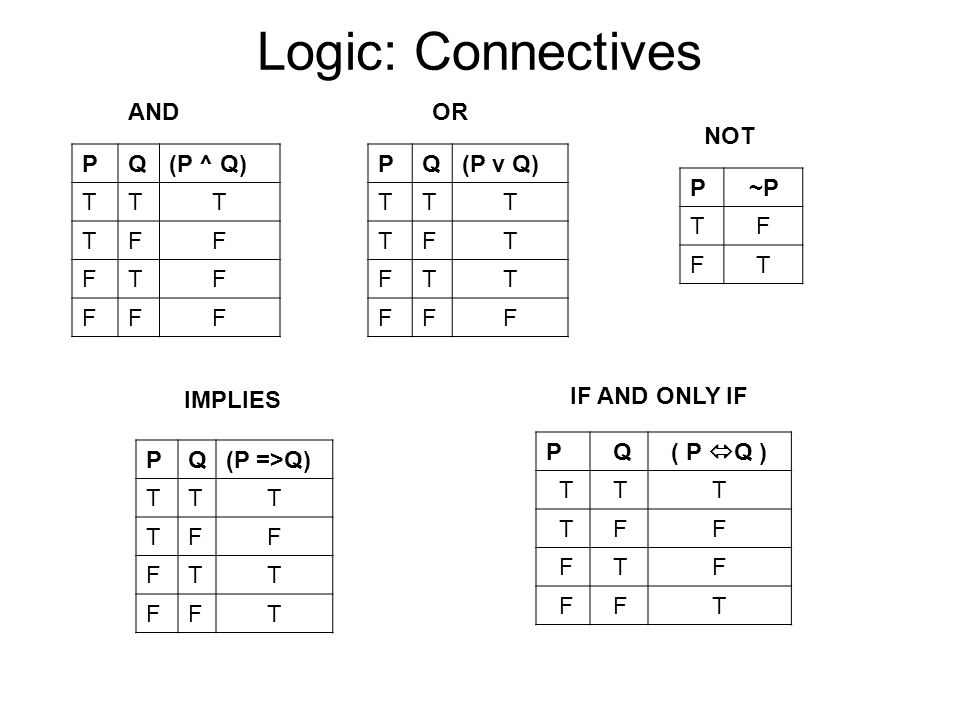
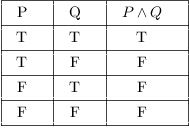
So if \(P\imp Q\) and \(P\) are both true, we see that \(Q\) must be true as well. In ordinary language terms, if both p and q are true, then the conjunction p ∧ q is true. The connectives ⊤ and ⊥ can be entered as T and F.
Here are a few more examples. For all other assignments of logical values to p and to q the conjunction p ∧ q is false. I will lower the taxes Think of it as a contract, obligation or pledge.
\begin{array}{cc|ccccc} p & q & p \vee q & \neg (p \vee q) & \neg p & \neg q & \neg p \wedge \neg q \\\hline T & T & T & F & F & F & F \\ T & F & T & F & F & T & F \\ F & T & T & F & T & F & F \\ F & F & F & T & T & T & T \\ \end{array} Since columns. Reminding someone to "watch his p's and q's" means to pay attention to the details. We know that T∧T ≡ T , T∧F ≡ F , F∧T ≡ F , F∧F ≡ F we know a∧b ≡ T in only 1 case that a ≡ T , b ≡ T.
I'll use '~' for negation, 'v' for disjunction, '&' for conjunction, '>' for implication, and '<>' for equivalence. Include A Truth Table And A Few Words Explaining How The Truth Table Supports Your Answer. (a) p !q q !p.
Think about when any of (P -> R) V (Q -> R) and (P ∧ Q) -> R are false:. P x 2 − q x 2 − (p x + q x) + 2 q = 0 To find the opposite of px+qx, find the opposite of each term. Simple and best practice solution for p-(p-q)-q-(q-p)= equation.
Said it will keep its full-year dividend payout unchanged at 13 yen per share, including an interim dividend of 6.50 yen. Q {\displaystyle p::q}, E p q {\displaystyle {\textsf {E}}pq}, or p q {\displaystyle p\iff q}, depending on the notation being used. Q.P.'s group net profit falls 22% in FY 05 Despite the drop in net profit, Q.P.
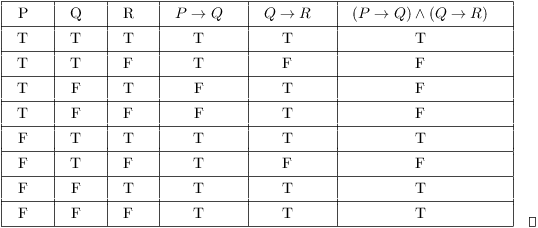
To find the opposite of p x + q x , find the opposite of each term. Since (p∨q)∧(p→ r)∧(q→ r) → ris always T, it is a tautology. Statements like q→~s or (r∧~p)→r or (q&rarr~p)∧(p↔r) have multiple logical connectives, so we will need to do them one step at a time using the order of operations we defined at the beginning of this lecture.
Now this only occurs if pis true and qis false. You could stop one step earlier by noticing that since the columns for :(p ^q) and :p _:q are identical, therefore they’re logically equivalent. Given p ⇒ q, use the Fitch System to prove ¬p ∨ q.
(15 points) Write each of the following three statements in the symbolic form and determine which pairs are logically equivalent a. Answers are given, but of course the idea is to come up with proofs of your own before looking them up. P∧(p→q)→q ≡ F therefore p∧(p→q) ≡ T , q ≡ F consider p∧(p→q) ≡ T a∧b truth table From a∧b truth table :.
Conduct (usually preceded by mind or watch):. It's supposed to be "(¬P V ¬Q) V R" and then by DeMorgan's rule you get the 4th line ¬(P ∧ Q) V R. Therefore, the statement ~pq is logically equivalent to the statement pq.
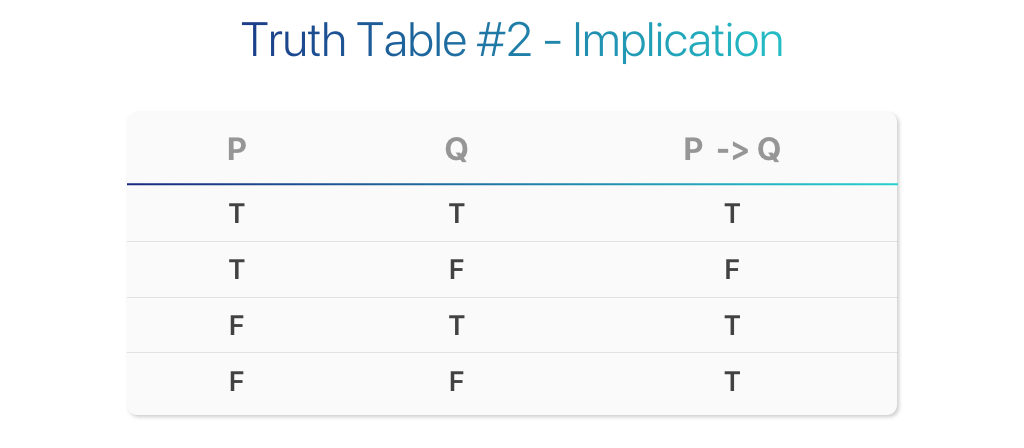
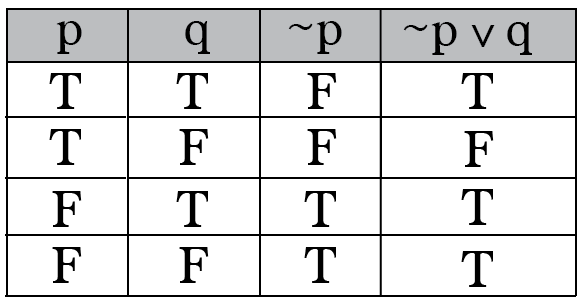
If it's not what You are looking for type in the equation solver your own equation and let us solve it. "p implies q is defined to mean that either p is false or q is true." The following truth table shows the logical equivalence of "If p then q" and "not p or q":. This enforces that the truth value of p and the truth value of q must always be the same.
P Q ∼ P ∼ Q P →∼ Q Q →∼ P P ∨ Q T T F F F F T T F F T T T T F T T F T T T F F T T T T F Consider The Argument Form:. Back in the early days of printing presses, each line of text had to be set up one letter at a time. Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future.
Math\begin{array}{|l} \llap{{1}\hskip{2.00em}} \rlap{\hskip. From an old printer's axiom. If p and q are logically equivalent, we denote the fact by p q 32.
If P and Q are two premises, we can use Conjunction rule to derive $ P \land Q $. ~pq If I don't study, then I fail. For example, the propositional formula p ∧ q → ¬r could be written as p /\ q -> ~r, as p and q => not r, or as p && q -> !r.
However, if pis true and qis false, then p^:qwill be true. P and q are true separately;. ~(P v Q) & (P > Q) P > Q is equivalent to.
P's and q's definition, manners;. ~(~p | q) Assumption 3. This tool generates truth tables for propositional logic formulas.
You can enter logical operators in several different formats. P q ~p ~pq pq T T F T T T F F T T F T T T T F F T F F In the truth table above, the last two columns have the same exact truth values!. Equivalent to finot p or qfl Ex.
How to Tell if the Structure of a Logical Argument is Valid. Our solution is simple, and easy to understand, so don`t hesitate to use it as a solution of your homework. (0 points), Page 35, problem 14.
P !q :p _q. P => q Premise 2. And if p then r;.
Breve explicación de un ejercicio de Equivalencias Lógicas - (~p V q) ⇔ (p ⇒ q). \(P\) is true in the first two rows, and of those, only the first row has \(P \imp Q\) true as well. In p !q, p is the hypothesis (antecedent or premise) and q is the conclusion (or consequence).
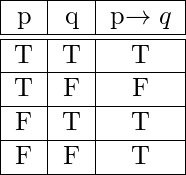
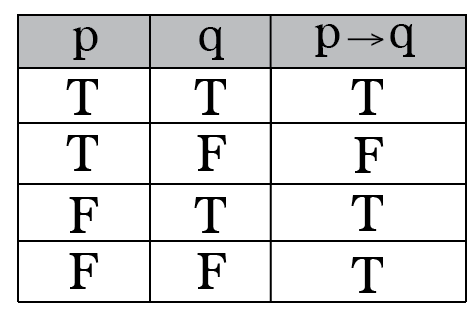
It can also be said that if p , then p ∧ q is q , otherwise p ∧ q is p. P → q (p implies q) (if p then q) is the proposition that is false when p is true and q is false and true otherwise. Solutions ECS (Winter 19) January 2, 19 Exercise 1 Construct a truth table for each of these compound propositions:.
Check how easy it is, and learn it for the future. The sentence ``if P and Not(P), then Q'' is always true, regardless of the truth values of P and Q. Find an answer to your question Given a conditional statement p → q, which statement is logically equivalent?.
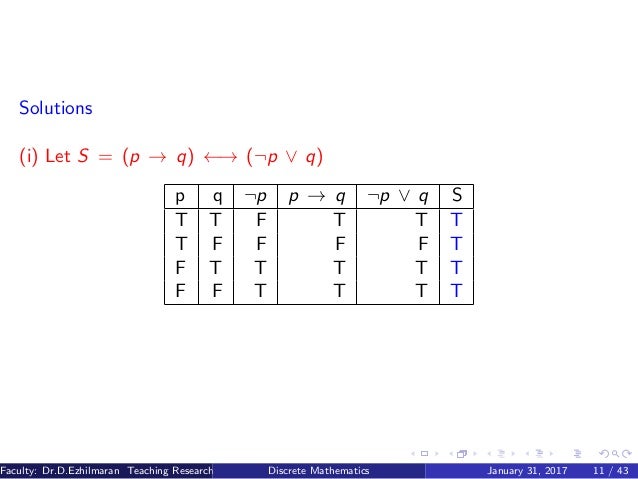
In an ``if---then'' sentence, if the sentence in. To check if $\neg (p \vee q)$ and $\neg p \wedge \neg q$ are logically equivalent:. ~p → ~q ~q → ~p q → p p → ~q evil1112 evil1112 05/25/16 Mathematics High School +5 pts.
Two propositions p and q are logically equivalent if p q is a tautology. Now, our final goal is to be able to fill in truth tables with more compound statements which have more than just one logical connective in them. P → q = (~p ∨ q) In the Principia Mathematica, the "=" denotes "is defined to mean." Using this denotation, the above expression can be read:.
And lo-and-behold, in this one case, \(Q\) is also true. This can be proven as follows:. If p and q are propositions, then p !q is a conditional statement or implication which is read as “if p, then q” and has this truth table:.
As for the intuitiveness of it. P q p→ q ¬p∧(p→ q) ¬p∧(p→ q) → ¬q T T T F T T F F F T F T T T F F F T T T So ¬p∧(p→ q) → ¬qis not a tautology.

If P Q Are Prime Positive Integers Prove That Root P Root Q Is An Irrational Number Mathematics Topperlearning Com 044i7v44
Logic 2 The Conditional And Biconditional Ppt Download
Logic Connectives And Or Not P Q P Q T F P Q P V Q T F P P T F Ppt Video Online Download
Pq+qp のギャラリー
Project Part 1 Nathan S Portfolio
Q Tbn 3aand9gctgeuarfw uu8usqijv9divozccab vrkkf235mcljj2g36 Usqp Cau
Show That Each Of These Conditional Statements Is A Tautology By Using Truth Tables A P P Q Q B P Q Q R P

Truth Table

1 5 2 Contradiction

Stpm Further Mathematics T 1 1 Logic

Formal Logic The Propositional Calculus Britannica
Show That Each Of These Conditional Statements Is A Tautology By Using Truth Tables A P P Q Q B P Q Q R P

Express 0 25 Bar In The Form Of P Q Brainly In
1
Solved Use The Deduction Method To Prove That 1 P Q R Chegg Com

Solution How Do You Write A Truth Table For The Statement Form P Q V Pvq

Formal Logic The Propositional Calculus Britannica
Logic Theory Truth Tables Part Iii Intro To The By Jesus Najera Towards Data Science
Propositional Logic Truth Table Boolean Algebra Dyclassroom Have Fun Learning

A Rational Number P Q Is Said To Be In The Standard Form Youtube
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsdfsw74km5frwxvudaqh2lx3eutrkp Hlwm8dqlovsiezdine7 Usqp Cau
9 If And Only If Using Theorems A Concise Introduction To Logic

Logic And Proofs
Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences

Proof And Problem Solving Truth Table Example 02 Youtube
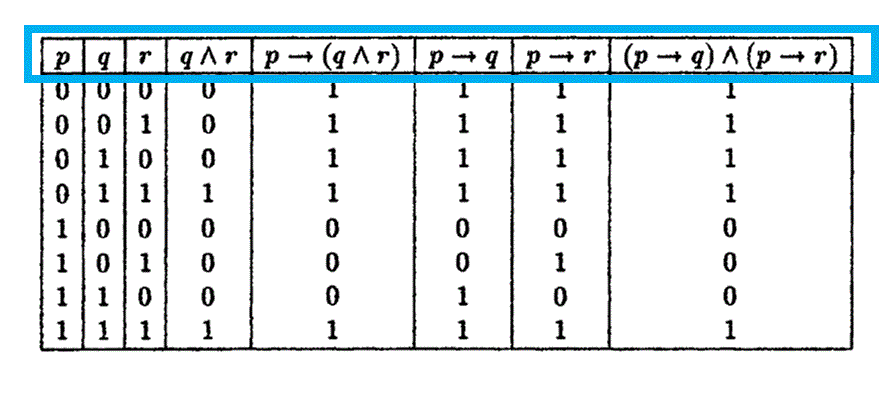
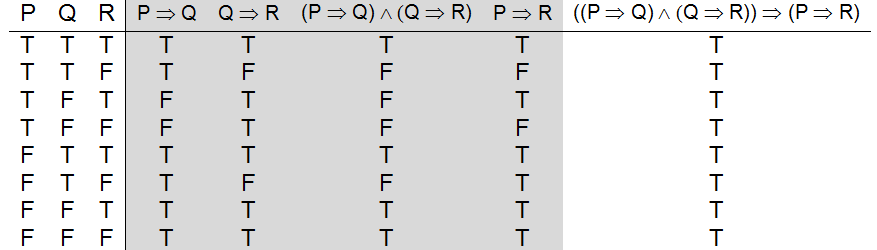
Let P Q R Denote Primitive Statements A Use Truth Tables To Verify The Following Logical Equivalences I Math Mathrm P Rightarrow Mathrm Q Wedge Mathrm R Leftrightarrow Mathrm P Rightarrow Mathrm Q Wedge Mathrm P Rightarrow

Formal Logic The Propositional Calculus Britannica
Truth Tables Section Ppt Video Online Download
How To Construct The Truth Table Of P Q Quora
Intro To Truth Tables Boolean Algebra By Brett Berry Math Hacks Medium
Truth Tables Of Compound Propositions
Propositional Logic

How To Change Operator Symbols In Truth Table Tex Latex Stack Exchange
Module 1 Discrete Mathematics And Graph Theory

Proving Logical Equivalence Involving The Biconditional Youtube
Www Studocu Com En Ca Document University Of Ottawa Discrete Mathematics For Computing Lecture Notes Mat1348 Notes 02 Filled View
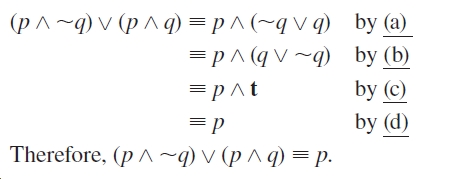
Answered Theorem 2 1 1 Logical Equivalences Bartleby

Chapter 12 Solutions
Http Eng Usf Edu Hady Courses Mgf1106 Documents Slides 3 3 Pdf

P Implies Q Discrete Mathematics For Dummies

Solved Show That Q P P Q Is A Tautology I E Q Chegg Com

If Pqr 1 Then Find The Value Of A Pq Qr Rp B 1 C Pq Qr D Mathematics Topperlearning Com 69iqzsrr

How To Prove P Q P Q Philosophy Stack Exchange
Module 1 Discrete Mathematics And Graph Theory
Watson

Mat1348 Notes 02 Filled Mat1348 Uottawa Studocu
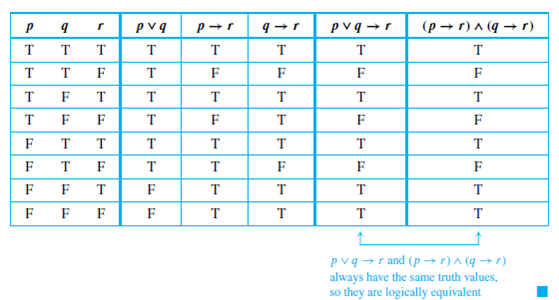
Solved Use The Logical Equivalence Established In Example To Chegg Com
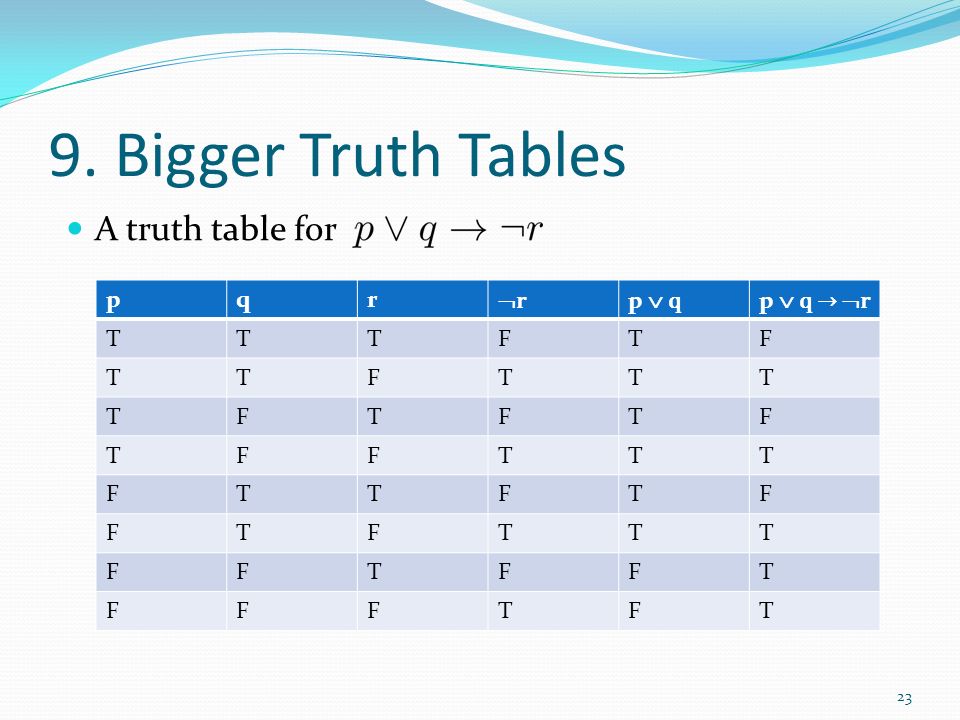
Discrete Maths 2 Propositional Logic Objective Ppt Video Online Download

Using The Fitch System How Do I Prove P Implies Q Implies P Implies P Mathematics Stack Exchange

Convert The Decimal Numbers Into The Form P Q I 18 48
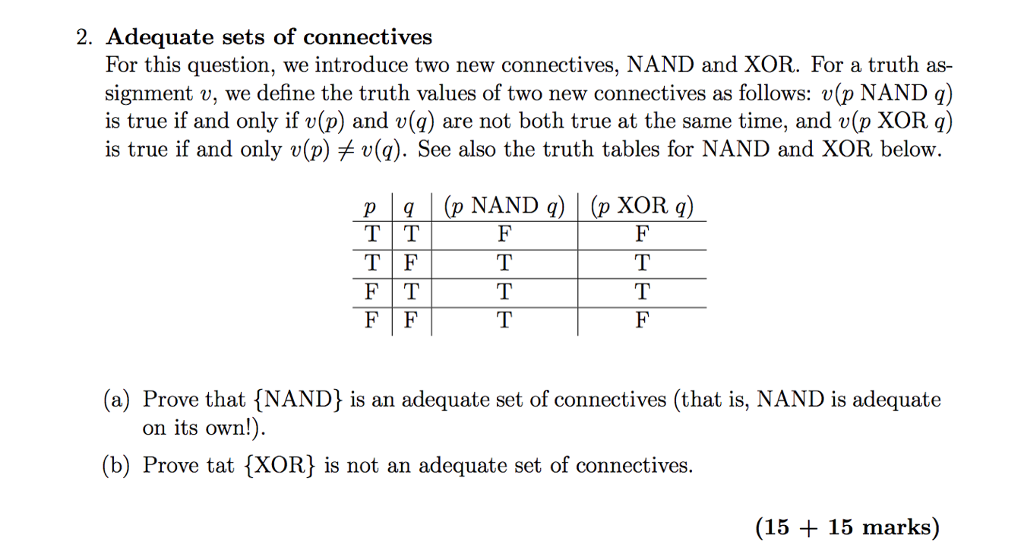
Solved P Q P Nand Q P Xor Q T T F F T F T T F T T T F Chegg Com
Http Www Math Drexel Edu Tolya Logicalequivalences Pdf

The Truth Table Represents Statements P Q And R Which Row Represent When P Q V P R Brainly Com
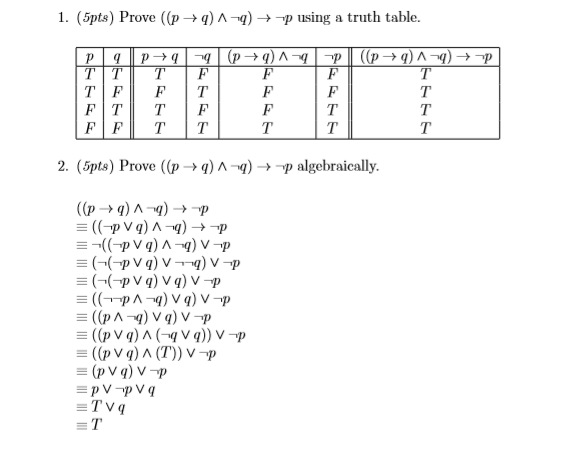
Solved 1 5pts Prove P Q A Q P Using A Truth Table Chegg Com

Logic Explainability And The Future Of Understanding Stephen Wolfram Writings

How To Find The Negation Of P Q P Implies Q Math Application Of Derivatives Meritnation Com

The Sheffer Stroke Internet Encyclopedia Of Philosophy
Mathematics Introduction To Propositional Logic Set 1 Geeksforgeeks
Www Researchgate Net Profile Noor Hilaly2 Publication Mathematical Theory For Social Scientists Links 5dd070cea6fdcc7ef Mathematical Theory For Social Scientists Pdf
Intro To Truth Tables Boolean Algebra By Brett Berry Math Hacks Medium

How To Find The Negation Of P Q P Implies Q Math Application Of Derivatives Meritnation Com
Mathematical Logic Part 2

Solve Partial Differential Equation F Zp X Y Q 2 Pq Z 2 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange

Chap 2 Fundamentals Of Logic Proposition Proposition Or Statement An Declarative Sentence That Is Either True Or False But Not Both E G Margret Ppt Download

Logic And Proofs

Converse Nonimplication Wikipedia
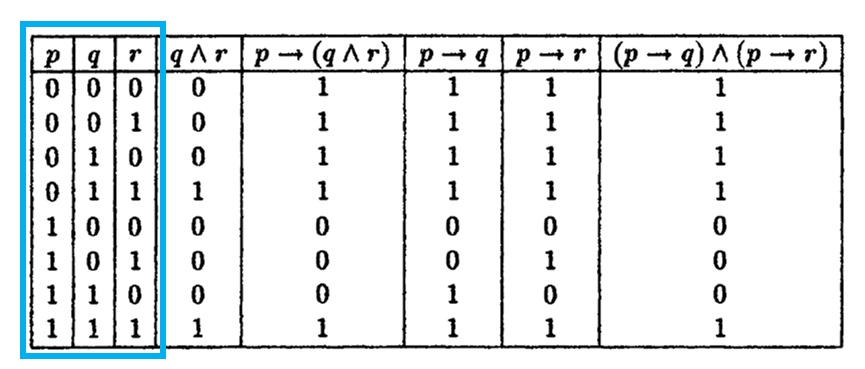
Let P Q R Denote Primitive Statements A Use Truth Tables To Verify The Following Logical Equivalences I Math Mathrm P Rightarrow Mathrm Q Wedge Mathrm R Leftrightarrow Mathrm P Rightarrow Mathrm Q Wedge Mathrm P Rightarrow

Negating The Conditional If Then Statement P Implies Q Mathbootcamps
Storm Cis Fordham Edu Zhang Cs2100 Slides Logic

17th Parts Logic Equiv P Q P R P Q R Youtube
Given P Q R And That R Is Perpendicular To P If P R Then What Is The Angle Between P And Q Quora
How To Solve P Q 4 P Q 4 8pq P 2 Q 2 Quora

Discrete Mathematics Lecture 1 Logic Of Compound Statements Ppt Video Online Download

Is P Land P To Q To Q A Tautology Mathematics Stack Exchange
Ppt Logical Equivalence Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Answered Theorem 2 1 1 Logical Equivalences Bartleby
Propositional Equivalences Ppt Video Online Download
Proof And Problem Solving Truth Table Example 02 Youtube
9 If And Only If Using Theorems A Concise Introduction To Logic
Show That Each Of These Conditional Statements Is A Tautology By Using Truth Tables A P P Q Q B P Q Q R P

Ex 9 3 5 A Add P P Q Q Q R And R R P Ex 9 3

Ex 9 2 11 Sum Of First P Q R Terms Of Ap Are A B C
Q Tbn 3aand9gctcyhof4gcdocwu6jlnli24t1p6nwxuwa4jtsdzykcgslzibwsm Usqp Cau

Logic Explainability And The Future Of Understanding Stephen Wolfram Writings
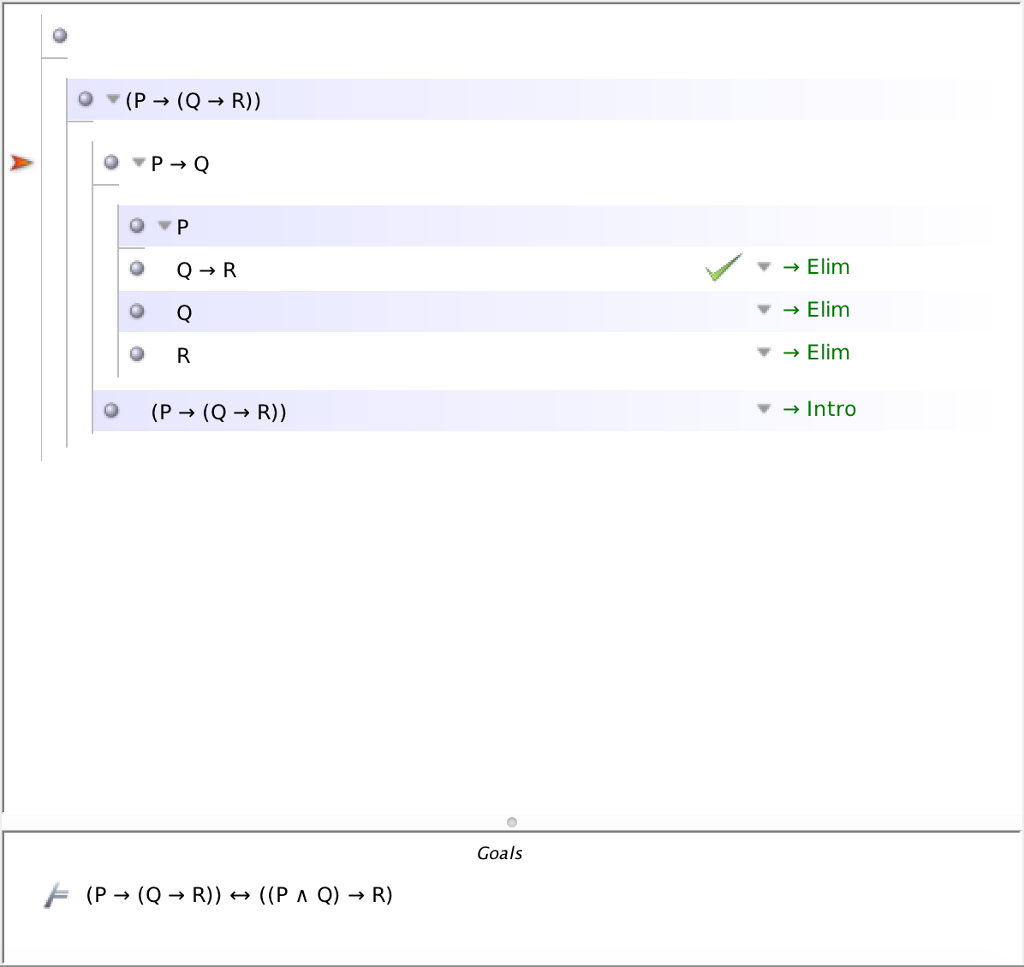
Solved Construct A Fitch Proof Of P Q R P Q Chegg Com

Best P Q Reversal Tips And Tricks Early Core Learning
Logic Truth Table For P Q R Q Youtube
Storm Cis Fordham Edu Zhang Cs2100 Slides Logic
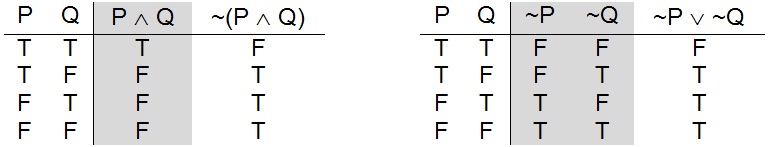
Watson
Solved Show That Q P P Q Is A Tautology I E Q Chegg Com

If P Is Not Equal To Q And P 2 5p 3 And Q 2 5q 3 The Equation Having Roots As P Q And Q P Is Brainly In
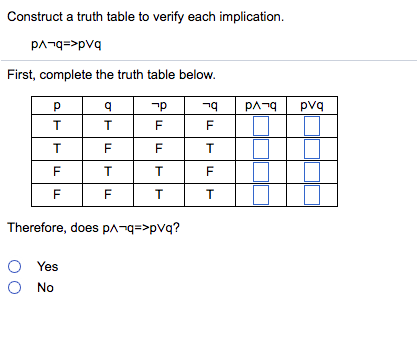
Solved Construct A Truth Table To Verify Each Implication Chegg Com

Negating The Conditional If Then Statement P Implies Q Mathbootcamps

Example 2 If P A B C And Q R Find P X Q And Q X P

Ex 14 3 4 Iii Divide 52pqr P Q Q R R P 104pq Q R
Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences

Conditional Statements If P Then Q Youtube
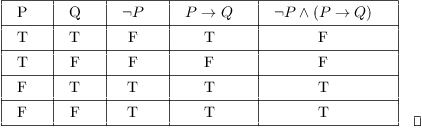
Truth Tables Tautologies And Logical Equivalences
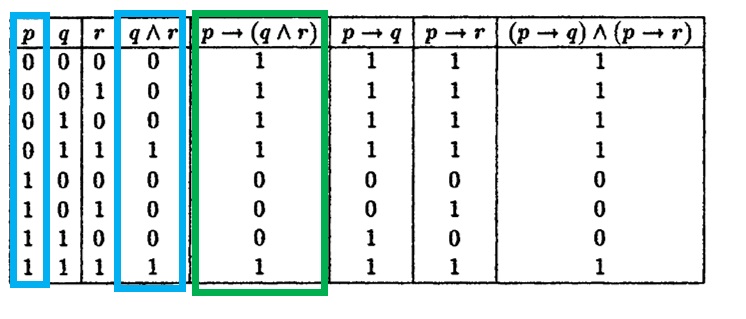
Let P Q R Denote Primitive Statements A Use Truth Tables To Verify The Following Logical Equivalences I Math Mathrm P Rightarrow Mathrm Q Wedge Mathrm R Leftrightarrow Mathrm P Rightarrow Mathrm Q Wedge Mathrm P Rightarrow
Http Storm Cis Fordham Edu Zhang Cs2100 Slides Logic Handout Pdf

Truth Table
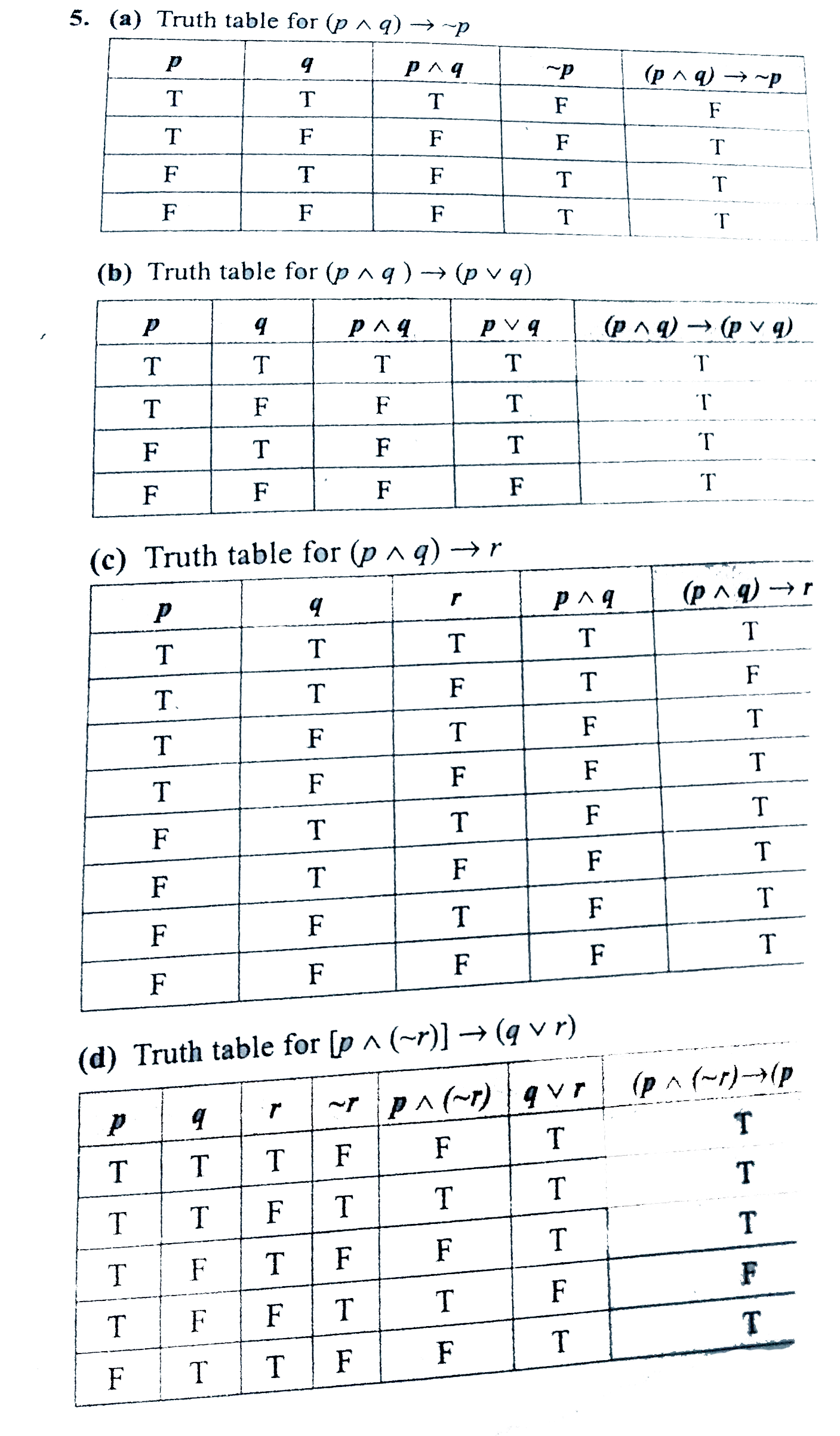
Construct The Truth Table For The Followings Statements Br A

Centromere Position In P Arm Or Q Arm Of Chromosome

Prove That P Oplus Q Oplus R Is Logically Equivalent To P Oplus Q Oplus R Mathematics Stack Exchange
Www Uplifteducation Org Cms Lib Tx Centricity Domain 291 Logic Practice 18 key Pdf




